What is coolant, what does it do, and how is it manufactured?
While coolant is a necessary component of a healthy engine, it is one that even professionals, countermen, repair technicians and fleet managers don’t fully understand. What are the different formulation types? Why does the pricing vary? How should you select the right coolant?
To understand what coolant is, and why it’s so important, we created Coolant University. Our 10 videos help provide answers to your questions about engine coolants.
Coolant is vital in order for an engine to operate reliably. It protects engines from freezing when parked, overheating when running, and corrosion inside the engine. Modern engines typically run hotter due to their design and materials, requiring improvements to cooling technology. Some vehicles park in extremely cold, sub-zero temperatures, requiring fluids that won’t freeze and damage the engine.
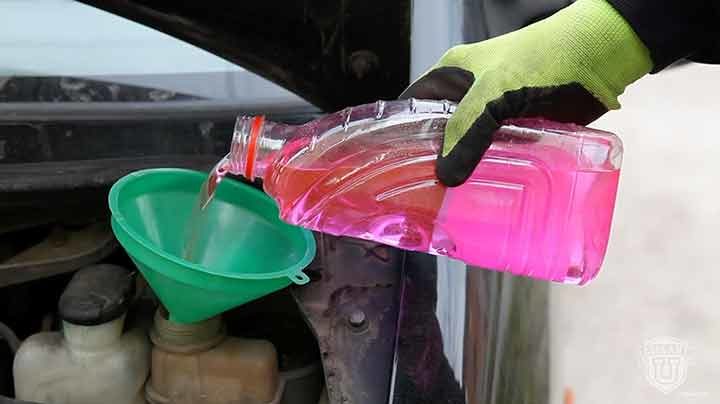
Coolant is made up of a mixture of two fluids – glycol and deionized water, plus special additives to prevent corrosion. When used in the vehicle’s cooling system they protect the engine from overheating and freezing.
What is Coolant, and What is Coolant Used For?
Coolant is a functional fluid that is essential for most engines to operate without overheating. Its primary purpose is to transfer heat inside an engine’s cooling system. While some engines are air-cooled, most engine designs use a liquid cooling system.
Engine coolant is a fluid that dissipates heat in-vehicle systems. It pumps through the engine block to absorb heat generated by combustion. The heated fluid is carried through hoses into a radiator where it is cooled by air circulation. To learn more about how coolant works and why it is so essential for your engine system, check out this video.
What is Coolant Made of?
Engine coolant is formulated by mixing water and glycol along with corrosion inhibitors which protect metal components.
Deionized water is used in all engine coolants because it is effective in absorbing heat. That being said, water has a freezing point of 0 degrees Celsius and boils at 100 degrees. This means that water alone won’t get the job done. This is why ethylene glycol is added to lower water’s freezing point and raise its boiling point.
To learn more about coolant composition, watch this video.
What Are Corrosion Inhibitors?
Corrosion inhibitors play an important role in modern coolant formulation. They are added to engine coolants to form a barrier that protects internal engine components from corrosion. Without the right inhibitor package, the lifespan of an engine can be significantly shortened.
There are 3 basic coolant technologies available on the market today:
- Conventional
- OAT
- Hybrid
The type of coolant right for your vehicle depends on the type of engine you have. This is because different types of engines (i.e. heavy-duty diesel engines vs. light duty) have different types of needs. To go more in-depth about corrosion inhibitors, check out this video.
Coolant is Always Evolving
Engine technology is constantly changing and evolving, with different varieties manufactured and used around the world. Because of this, coolant technology is always evolving to meet the demands of global markets.
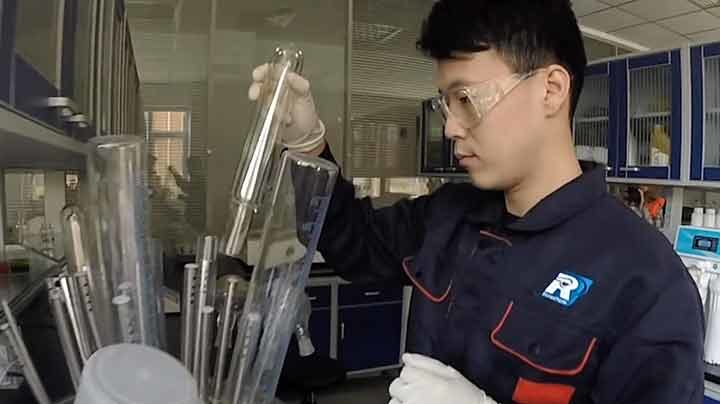
Not only has the technology evolved, but the means we have to test it has as well. Given coolant degrades over time, the use of PH testing and Specific Gravity Testing has been developed in order to quality check coolant in vehicles.
To learn more about how modern coolant technology has evolved around the world, click here.
Coolant University Can Help You Understand Everything You Need to Know About Coolant
Whether you are a fleet manager, parts professional, repair tech, or a DIY hero, keeping track of all the coolant choices on the market can be tough. That’s why we created Coolant University.
Coolant U is a video series that helps people become coolant solutions experts. We have easy-to-understand, informative modules that take you from the basics of coolant, to formulation, to global manufacturing, and more. Once you have watched all of our videos, you can visit our HD Expert website to browse and purchase our ideal coolant solutions.
Click here to learn more.
Did you find this useful? Check out the next 3 modules in our video series:
Module 5: Light-Duty vs. Heavy-Duty Usage
Module 6: Light-Duty Coolant Technology
Module 7: Light-Duty Coolant Formulations